Start monitoring today.
Begin monitoring threat intelligence to act before attackers do.
Get Started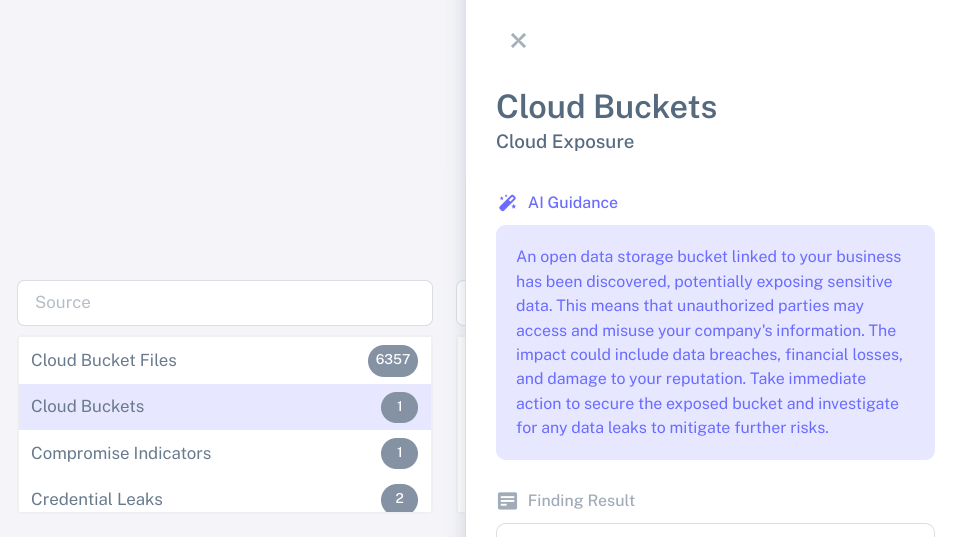
2024-11-04 ThreatHarvest Blog Strategy
Effective cyber threat intelligence is integral to cybersecurity, yet small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) may not always choose the best path with their approach. A host of obstacles often prevents the success of such efforts. Below are the top five mistakes people routinely make in cyber threat intelligence along with solutions for strengthening an intelligence practice.
The biggest mistake in cyber threat intelligence is to ignore PIRs. These are the main questions any organization wants to answer through gathering intelligence. Organizations must focus on what information is important to their unique environment to avoid drowning in irrelevant data. To solve this problem, SMBs must carefully choose their PIRs to suit the characteristics of their organization and its environment.
Another major mistake with cyber threat intelligence is to overlook the stakeholders within an organization. Cybersecurity is a jointly managed outcome requiring the cooperation of technology professionals, leadership, and employees. A team-based approach provides a more comprehensive perspective on potential threats and encourages SMBs to review threat findings and develop defense strategies from several angles.
Threats evolve at breakneck speed. Relying on manual data collection and tracking methods is not a sustainable approach. Automating these processes greatly increases the accuracy, efficiency, and productivity of cyber threat intelligence programs. SMBs can use services such as ThreatHarvest to streamline data analysis, such that they can respond rapidly with appropriate countermeasures when threats arise. Focus is best spent on the findings rather than on the mechanics of collecting and processing data.
SMBs can fall into the trap of seeing cyber threat intelligence as a one-off or ad-hoc activity. They only run one report and feel that their defenses are adequate. Threat intelligence is most useful when necessary action is taken promptly after new information is learned. Without ongoing monitoring, there is no visibility into the changing threat landscape. Thus, a static approach exposes businesses. Because threats and vulnerabilities arise continuously, continuous monitoring is needed to keep pace. Regularly updating and improving intelligence strategies will keep organizations adapting to changes in the cyber threat landscape.
Identifying and maintaining relevant sources of threat intelligence data can be a significant challenge for SMBs. These activities can require specialized expertise with appropriate judgment to find the most relevant sources. Insufficient data from multiple low-quality sources weakens the effectiveness of threat assessment. The dependence on limited avenues or low-quality data may lead organizations to miss out on significant insights.
To receive the complete benefits of cyber threat intelligence, organizations should steer clear of the common pitfalls listed above. By carefully choosing and fine-tuning priority intelligence requirements, encouraging teamwork, automating processes, implementing continuous monitoring and identifying appropriate data collection channels; SMBs can fortify their digital defenses.
Begin monitoring threat intelligence to act before attackers do.
Get Started